Concatenated Indexes and Index column order
A concatenated index, also known as multi-column, composite or combined index, is one index across multiple columns. In case of queries with multiple equality conditions, even though multiple single c...

A concatenated index, also known as multi-column, composite or combined index, is one index across multiple columns. In case of queries with multiple equality conditions, even though multiple single c...
Performance of a query having multiple equality type predicates improves as it switches from using the index on an unselective column to a selective one. It is very common to issue queries with multi...
The selectivity of an index is defined as the fraction of rows in a table having the same value for the indexed key. A highly selective index has few rows for each index entry and an unselective inde...
In Part I of this article, I discussed the Cluster administrator’s view of the What-If Command Evaluation and demonstrated how cluster administrators can use crsctl to Perform What-If Command Evalu...
Cluster administrators are expected to perform management operations on the cluster which may be hosting various applications and databases. Prior to Oracle clusterware 12c, the effects of cluster man...
Oracle 12c introduces full transportable export/import, an exciting new feature that greatly simplifies the process of database migration. It allows you to upgrade or migrate to Oracle Database 12c ...
Oracle Database 12c has introduced Oracle Flex Cluster which allows management of applications and the RDBMS in a common cluster using the Hub-Leaf deployment model. The database tier is composed of '...
A B-Tree index – short for balanced tree index – is typically the most common type of index found in most Oracle databases. Just like the index of a book, it stores the values in the indexed column(s)...
I have been exploring Oracle multitenant application containers and sharing my learning by means of a series of articles for about a year now. This is the concluding article in the series, in which I ...
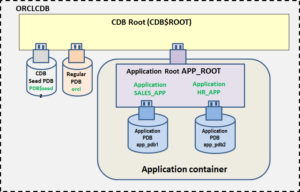
An Oracle multitenant application container can house multiple applications. These applications may be shared by various application PDBs within the container. Each of these applications can have comm...
As we learnt in my previous article in this series, with the introduction of Oracle multitenant application containers in Oracle Database 12.2.0.1, a user can create a common user in the CDB root or i...
Prior to Oracle database 12.2.0.1, there could be following types of users in an Oracle multitenant container database (CDB) – Common User – A common user is created in the CDB root and has the same...